A patient presents at 38-weeks gestation with complaints of decreased fetal movement and ruptured membranes. The fetal heart rate is not able to be determined with an external ultrasound monitor. A spiral electrode is placed, and the tracing shows a rate of 90 bpm. What is the next most appropriate action?
When the fetal heart rate is measured by a Doppler transducer and the intervals between heart beats are persistently identical, this shows as
Sustained fetal supraventricular tachycardia that goes untreated is most likely to result in:
A fetal heart rate pattern characteristic of fetal neurological injury and impending intrapartum fetal demise is:
(Full question statement)
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends continuous electronic fetal monitoring in pregnancies when there is:
(Full question statement)
A dysrhythmia is noted. The pregnancy and labor course has been normal with no complications. The next step in management is to
A sentinel or reportable event as defined by the Joint Commission or other regulatory bodies/agencies is one that
A key differentiating factor when determining if a deceleration is early or late is the
During the second stage of labor, a period of bradycardia develops. The fetal heart rate baseline variability is moderate. The most likely cause of this bradycardia is:
A woman at 41-weeks gestation is being induced. She is 2 cm dilated and is on oxytocin at 8 milliunits/minute. Based on the fetal heart rate tracing shown, the best initial response is to:
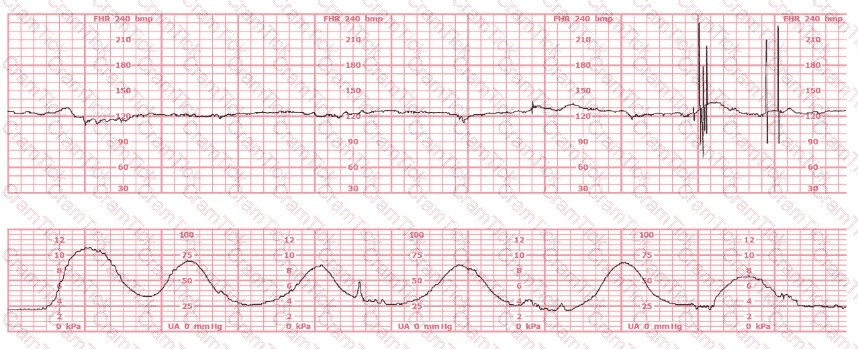
A woman has been 5 cm dilated for the past 3 hours. The tracing shown has developed over the last 30 minutes. The best initial course of action is to:
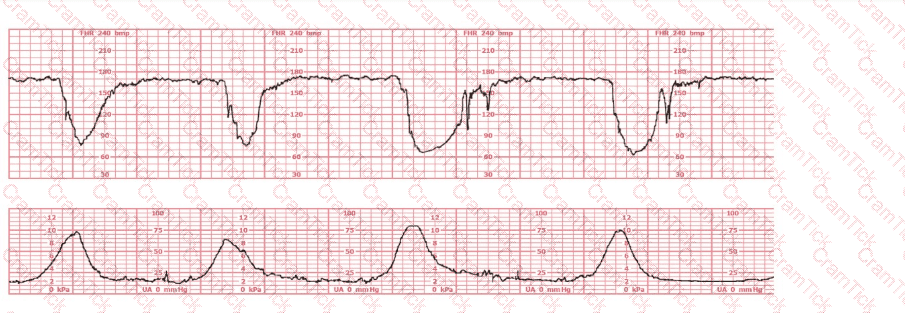
This is a fetal heart rate tracing of a multiparous woman whose cervix is 7 cm dilated on admission. The most likely cause for this pattern is:
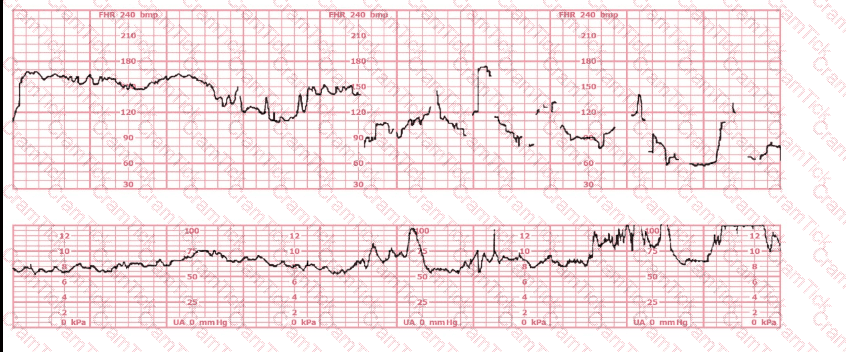
(Full question)
Vibroacoustic stimulation (VAS) is a useful intervention which can
A woman who is one week past a confirmed due date has serial ultrasounds to determine:
A 30-year-old woman (G2P0) is experiencing preterm labor at 26-weeks gestation. She is receiving magnesium sulfate for neuroprotection. Her external fetal monitoring tracing over the past 30 minutes is shown. The next step would be to:
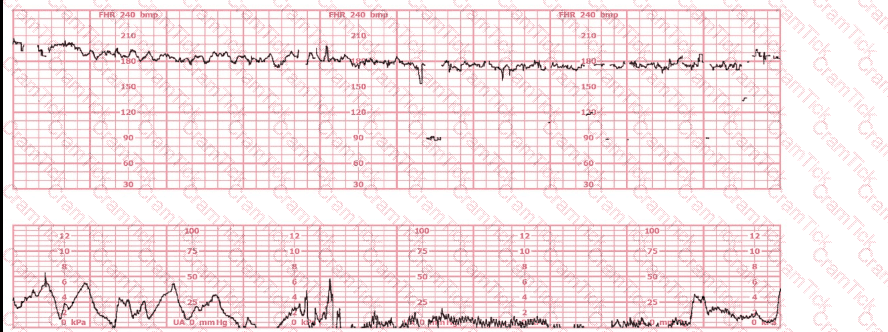
This fetal heart rate tracing is from a woman in the second stage of labor. This tracing is best interpreted as:
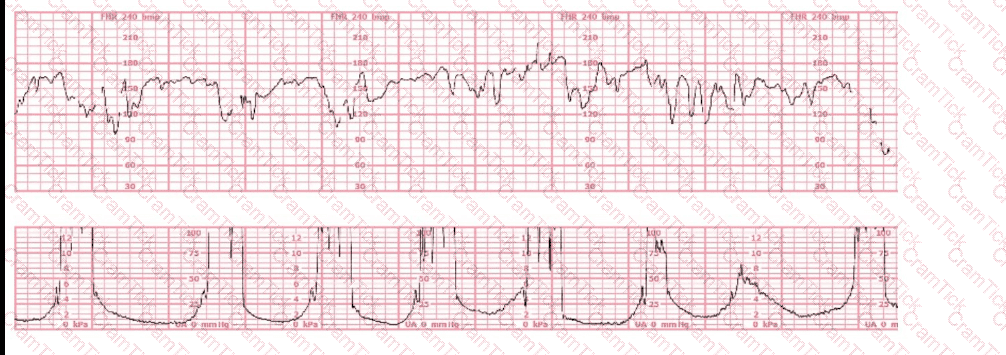
Nonstress testing is used more frequently for antepartum testing than contraction stress testing because contraction stress testing has a:
(Full question statement)
Recurrent decelerations are defined as occurring with 50% or more of contractions in any window of how many minutes?
Intermittent fetal heart rate auscultation for a low-risk, spontaneous laboring patient who is 4–5 centimeters dilated should be assessed at intervals every
A fetus displays a baseline heart rate of 125 beats per minute with moderate variability. During a contraction, the baseline rate drops abruptly to 80 beats per minute with gradual return to baseline over 90 seconds. This is classified as:
Maternal conditions of autoimmunity can result in fetal heart block due to antibodies that target:
A fetal heart rate tracing is abnormal. A change in maternal position and oxygen administration do not correct the pattern. Following birth, a fetal cord blood sample is taken:
pH = 7.25
PaCO₂ = 46 mm Hg
PaO₂ = 20 mm Hg
HCO₃ = 22 mEq/L
Base deficit = –4 mEq/L
These results are best interpreted as:
C-EFM |


